- Return to book
- Review this book
- About the author
- Introduction
- 1. Android
- 2. TDD with Robolectric
- 3. Architecture
- 4. Fundamentals
- 5. Resource System
- 6. Managing the Lifecycle
- 7. Lab: Calculator
- 8. Appendix
- 9. Epilogue
- 10. About The Author
- 11. Bibliography
Model View Controller
There are abstractions at every level to help you separate concerns, maintain code easier, and support the multitude of devices and form factors in the wild. Android gives you tools to to decouple the presentation layer from the business logic.
Although some argue that Android is not a true MVC system, it's helpful to approach it in this way.
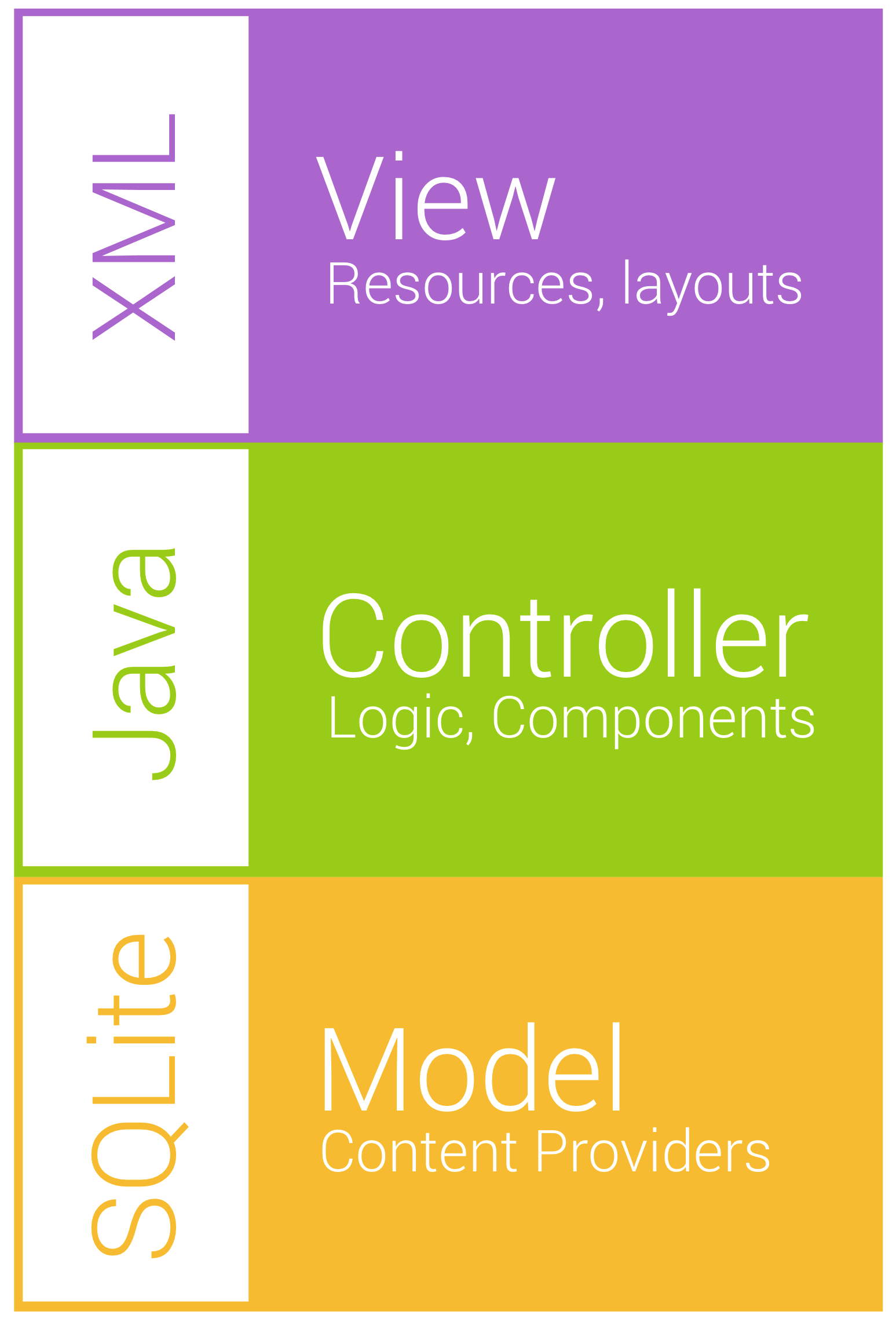
View
The view and resource system allows us to break out visual components. Android automatically handles most of the logic about choosing which component to use for which form factor. You specify this in XML and put in special folders. This enables scaling to different form factors as well as internationalization.
Controller
The Java layer is where you tie the visual components to the business logic of your application and where you would access the model or data of your system. Services would also fall into this layer.
Model
Finally, the model layer is where you would store the data that powers the application. Content providers allow you to abstract SQL queries away from your model's users and surface data throughout the application and system wide, if you desire.